Surgery for Hip Deformities
Hip deformities are common in pediatric cerebral palsy and can be corrected, at least partially, through appropriate surgical interventions.
WHAT ARE HIP DEFORMITIES?
One of the most challenging deformities in Pediatric Cerebral Palsy is hip dislocation. Unlike congenital forms present at birth, neurological dislocation emerges during growth.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF HIP DEFORMITY?
The neurological condition of cerebral palsy predisposes individuals to hip deformities, influenced by factors such as:
- Severity of neurological impairment, more common in non-ambulatory children.
- Imbalance in pelvic muscle forces, affecting adductor and flexor muscles due to spasticity.
- Adoption of compromised positions due to inadequate overall postural control.
- Non-weight-bearing on the femur in non-ambulatory patients leading to the straightening of the femoral neck (cephalic valgus).
- Abnormal development of the acetabular cavity, which receives the femoral head, turning vertical and exposing the femoral head.
TYPES OF HIP DEFORMITIES
Depending on the degree of joint incongruence, two forms are distinguished:
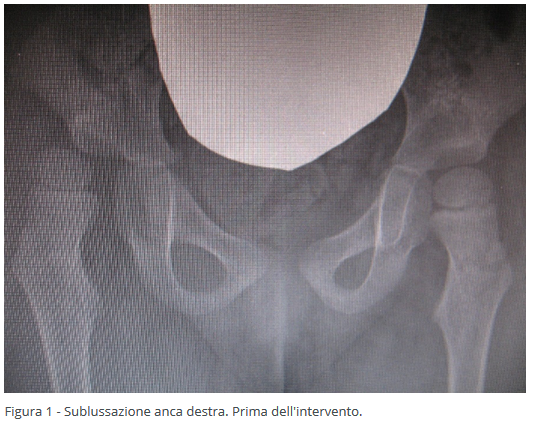
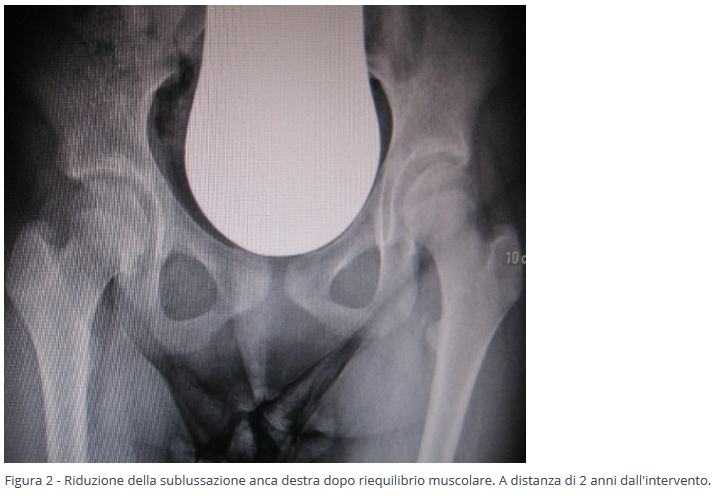
- Subluxation, where there's a partial loss of congruence between the acetabular cavity and the femoral head.
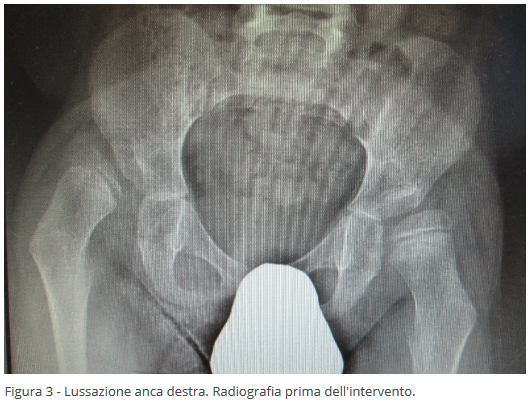
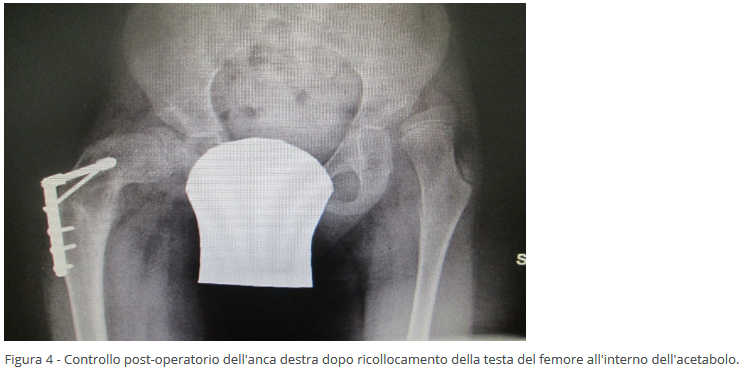
- Dislocation, where there's a complete loss of congruence between the acetabular cavity and the femoral head.
RECOMMENDED MEASURES
Internationally defined guidelines emphasize preventing hip dislocation through regular clinical and radiographic checks, intervening early when deformities manifest to prevent worsening. Hip dislocation causes severe joint damage, leading to cartilage wear, resulting in progressively worsening painful symptoms.
Due to spastic muscle tension, the dislocated hip continues to ascend, causing significant friction between the femoral head and the pelvis. This leads to restricted hip joint movements, adduction and flexion of the thigh, challenges in managing rehabilitative care, hygiene difficulties, and postural issues. The resultant pelvic imbalance often contributes to the development of scoliosis.
WHEN AND HOW TREAT HIP DEFORMITIES
When conservative treatment (physical therapy, muscle relaxants) for pediatric cerebral palsy fails to counter the progression of hip deformities, early surgical intervention becomes necessary.
In the presence of spasticity, the initial surgical approach focuses on soft tissues, reducing tension in predominant muscles (adductors and possibly the psoas). This minimally invasive surgery, often done percutaneously through fibrotomy, allows for quick recovery. Restoring muscle balance helps halt or slow damage caused by overactive muscles pulling the femoral head out of the acetabular cavity. This intervention can be performed at a very young age (2-3 years).
Surgical intervention on bone structures may involve the femur or both the femur and acetabulum, depending on the anatomical damage. This invasive surgery, using controlled fractures, reconstructs the correct positioning of the femoral neck and acetabular cavity, allowing the femoral head to be properly accommodated. A cast is applied post-surgery to facilitate fracture healing. This intervention is typically recommended after the age of 6.
In older children where relocating the femoral head within the acetabulum is no longer feasible, surgery involves resection and removal of the femoral head to eliminate friction between the femoral head and the pelvis. This procedure is generally performed after the age of 15, providing complete pain resolution and restoration of thigh movements.
Written by: Pier Francesco Costici, Rosa Russo - Orthopedics Operational Unit in collaboration with: Bambino Gesù Institute for Health
original article from ospedalebambinogesù.it